- LCS v.2 operating principle
- Operation
- Operating functions
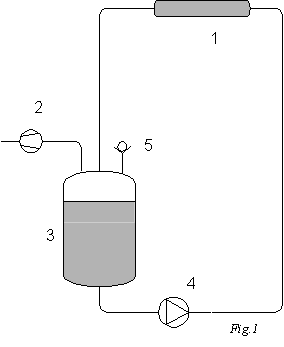
| The liquid is held in a storage
tank (3) maintained below atmospheric pressure by a vacuum pump (2). A
check valve discharges any excess air in the event of drainage and prevents
the pressure in the storage tank from rising above atmospheric pressure.
The liquid is moved into the exchangers (1) incorporated through the
electronic system by a circulator (4).
The pressure at the various points of the circuit depends on the head losses and hydrostatic pressures. At start-up, if the pressure in the storage tank is not low enough the vacuum pump is activated. While the later is in operation, in the event of an air intake for instance, the circulator cannot run. The pressure throughout the circuit still equal to the pressure in the storage tank. |
 |
The liquid is held in the storage tank below atmospheric and
this pressure is controlled by the vacuum pump via a pressure switch.
A second switch fixes a maximum pressure point to stop the circulator (case of main leak).
The whole system is stopped and needs to be resetted if the vacuum pump works for more than 20 minutes.
If the pressure value is contained between the operating setting point and the upper point (switching difference) the circulator and the temperature regulation (controller and heater) run. The vacuum pump and the electrovalve are off. This is the running mode.
If the pressure goes higher than the upper point of the vacuum switch the vacuum pump starts, the 3 ways electrovalve is actuated after 2 sec. and the pressure goes down to the lowest setting point pressure (the minimum admissible pressure). The circulator and the temperature regulation are still running.
A manual vacuum pump switch lets the operator to active it in order to gas out the circuit or to fill the storage tank with fluid (3 positions switch on PPV).
The outlet pressure of the circulator is controlled by a pressure sensor via the PID 3-phase frequency converter. The set point can be adjusted by a manual potentiometer (Pump setpoint).